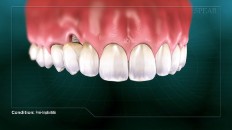
 Peri-implantitis is a disease characterized by the inflammation of gum tissue and bone around a dental implant, resulting in the loss of the supporting bone around it. Oftentimes you may not be aware this is occurring, and it is important to seek treatment for the condition if it is detected.
Peri-implantitis is a disease characterized by the inflammation of gum tissue and bone around a dental implant, resulting in the loss of the supporting bone around it. Oftentimes you may not be aware this is occurring, and it is important to seek treatment for the condition if it is detected.
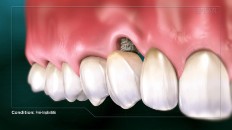 Symptoms of peri-implantitis can vary in type and severity. Some symptoms include redness, inflammation, and bleeding of the surrounding gum tissue, deepening of the periodontal pockets around the implant, exposure and visibility of the underlying implant threads, loosening of the implant itself, and pus discharging from the tissues around the implant. In cases of more severe infection, the lymph nodes on your neck may become swollen as well.
Symptoms of peri-implantitis can vary in type and severity. Some symptoms include redness, inflammation, and bleeding of the surrounding gum tissue, deepening of the periodontal pockets around the implant, exposure and visibility of the underlying implant threads, loosening of the implant itself, and pus discharging from the tissues around the implant. In cases of more severe infection, the lymph nodes on your neck may become swollen as well.
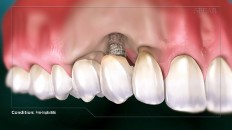 The most common cause of peri-implantitis is tartar buildup at the implant site, which harbors toxin-emitting bacteria that cause irritation of the surrounding gum tissue, and ultimately results in tissue and bone loss. There are other possible causes that may apply depending on your situation.
The most common cause of peri-implantitis is tartar buildup at the implant site, which harbors toxin-emitting bacteria that cause irritation of the surrounding gum tissue, and ultimately results in tissue and bone loss. There are other possible causes that may apply depending on your situation.
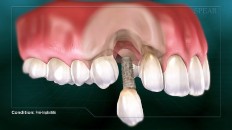 If left untreated, the infection and bone loss can progress to a point that the implant does not respond to treatment, and could lead to loss of the implant altogether.
If left untreated, the infection and bone loss can progress to a point that the implant does not respond to treatment, and could lead to loss of the implant altogether.
 If addressed early enough, there are treatment options available to halt the progression of the disease and attempt to repair the damage. It is important to work closely with a dentist experienced in treating this condition to determine the best options with the highest likelihood of success.
If addressed early enough, there are treatment options available to halt the progression of the disease and attempt to repair the damage. It is important to work closely with a dentist experienced in treating this condition to determine the best options with the highest likelihood of success.
Copyright © 2016 Spear Education. All rights reserved.